Do Diesel Engines Use Spark Plugs?
When it comes to the question of whether diesel engines use spark plugs, the answer may surprise you. Contrary to gasoline engines, diesel engines do not rely on spark plugs to ignite the fuel-air mixture. Instead, they use a different method called compression ignition, where the high pressure and temperature created by compressing the air in the combustion chamber causes the diesel fuel to ignite spontaneously.
This unique characteristic of diesel engines sets them apart from their gasoline counterparts. The absence of spark plugs in diesel engines eliminates the need for an external ignition system and allows for a simpler design. This simplicity contributes to the durability and reliability of diesel engines, making them well-suited for heavy-duty applications such as in trucks, ships, and industrial machinery.
Diesel engines do not use spark plugs like gasoline engines do. Instead, they rely on the heat of compressed air to ignite the fuel in the combustion chamber. This is known as compression ignition. In a diesel engine, the air is compressed to a high pressure and temperature, causing the fuel to ignite spontaneously. This design results in better fuel efficiency and greater torque compared to gasoline engines. So, no, diesel engines do not require spark plugs.
How Diesel Engines Work: A Unique Perspective
When it comes to engines, most people think of spark plugs as an essential component for igniting the fuel-air mixture. However, there’s a common question that arises when considering diesel engines: “Do diesel engines use spark plugs?” The answer may surprise you. Unlike gasoline engines, diesel engines rely on a different ignition process that doesn’t require spark plugs. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of diesel engines and explore how they operate without the need for traditional spark plugs.
The Compression Ignition Principle of Diesel Engines
To understand why diesel engines don’t use spark plugs, we need to explore their unique combustion process known as compression ignition. Unlike gasoline engines that rely on spark plugs to initiate combustion, diesel engines use the heat generated by the compression of the air-fuel mixture to ignite the fuel. This combustion process is known as the compression ignition principle, and it is the key difference between diesel and gasoline engines.
Compression ignition occurs in diesel engines when the air-fuel mixture is compressed to such a high pressure that it becomes hot enough to ignite the diesel fuel. As the piston moves up, compressing the air and fuel in the combustion chamber, the temperature rises significantly. At the top of the compression stroke, the fuel injector sprays a fine mist of diesel fuel into the hot, pressurized air. The heat from the compressed air causes the fuel droplets to ignite, starting the combustion process.
Due to the high compression ratios in diesel engines, the air-fuel mixture reaches temperatures hot enough to self-ignite at around 700 degrees Celsius (1292 degrees Fahrenheit). This eliminates the need for spark plugs since the combustion is initiated purely through the extreme heat generated by compression. The compression ignition principle is what makes diesel engines more efficient in terms of fuel consumption compared to gasoline engines.
Benefits of Compression Ignition in Diesel Engines
The use of compression ignition in diesel engines brings several advantages:
- Higher efficiency: Diesel engines operate at higher compression ratios, leading to improved thermal efficiency and better fuel economy.
- Increased torque: The combustion process in diesel engines generates higher torque, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications such as towing and hauling.
- Lower fuel consumption: The efficient combustion process in diesel engines results in lower fuel consumption, making them more cost-effective in the long run.
- Reduced carbon dioxide emissions: Diesel engines produce less carbon dioxide per mile traveled, contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
By harnessing the power of compression ignition, diesel engines offer a unique set of advantages that make them popular in various industries, including transportation, construction, and agriculture.
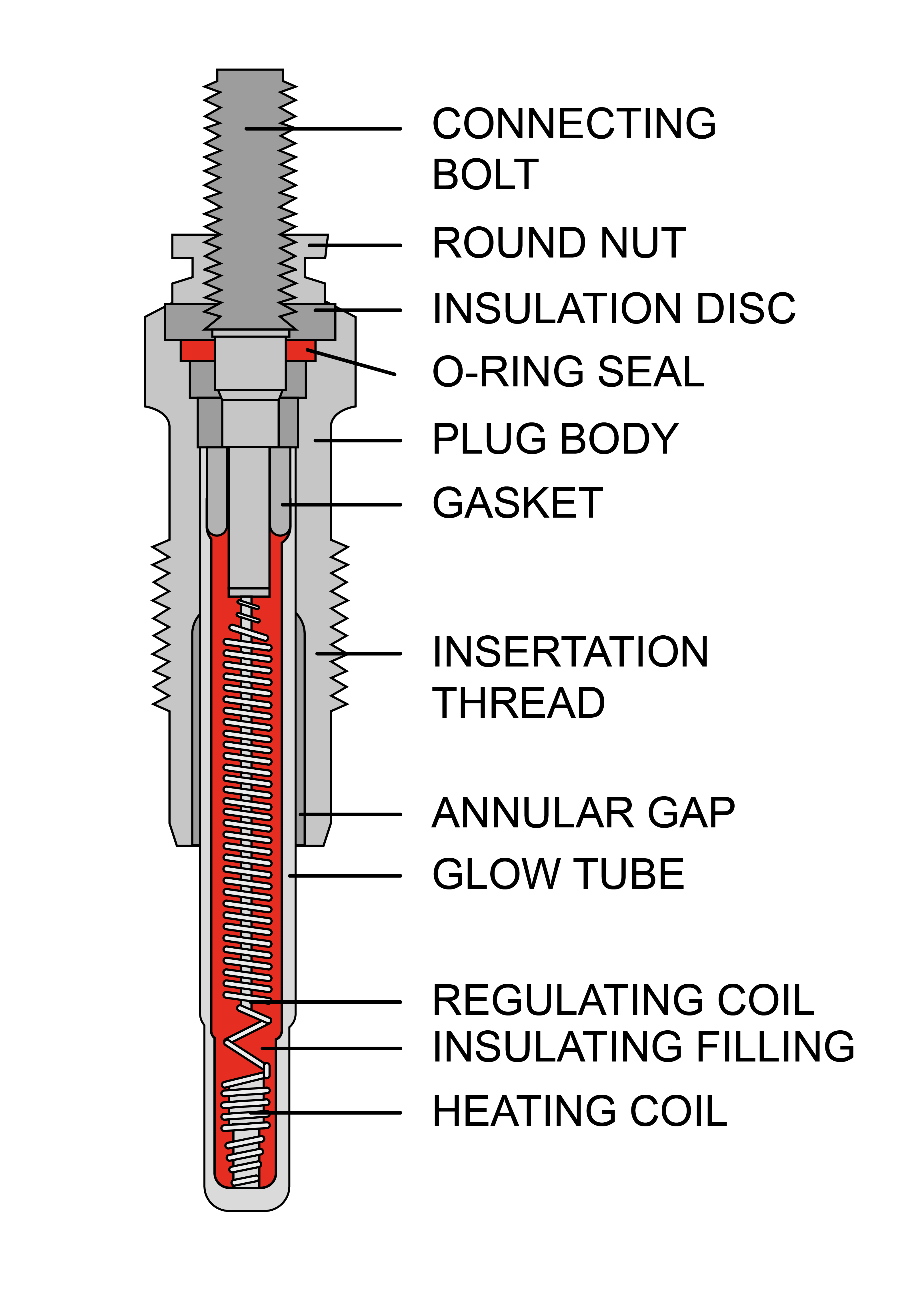
The Role of Glow Plugs in Diesel Engines
Although diesel engines don’t use spark plugs for ignition, there is still a component that aids in the combustion process: glow plugs. Glow plugs are used in diesel engines to preheat the combustion chamber, especially during cold starts. They function similarly to the heating element in an electric oven, helping to raise the temperature of the compressed air in the cylinder. This preheating process ensures that the air-fuel mixture reaches the necessary temperature for self-ignition, even in cold weather conditions.
Glow plugs are typically made of a heating element encased in a protective sheath. When activated, the heating element heats up and glows red-hot. This heat is transferred to the combustion chamber, raising the air temperature and aiding in the compression ignition process. Once the engine reaches its operating temperature, glow plugs are no longer necessary and turn off automatically. However, they play a critical role in ensuring a smooth ignition process in diesel engines, especially in colder climates.
Ignition Timing in Diesel Engines
Another crucial aspect of diesel engines that differentiates them from gasoline engines is ignition timing. Ignition timing refers to the precise moment when the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber. In gasoline engines, this timing is determined by the spark plug, which ignites the fuel at a specific point in the engine’s cycle. However, in diesel engines, the injection timing plays a critical role in achieving optimal combustion.
The timing of fuel injection in diesel engines is carefully controlled by the engine control unit (ECU) based on various factors such as engine load, RPM, and driver inputs. The goal is to inject the fuel at the right moment, when the piston is near the top dead center, to optimize power output and minimize emissions. By precisely controlling the injection timing, diesel engines can achieve better fuel efficiency and reduce pollutants.
The ability to control injection timing is one of the advantages of diesel engines over gasoline engines. It allows for better optimization of the combustion process, resulting in improved performance and lower emissions. The precise timing of fuel injection, along with the compression ignition principle, contributes to the overall efficiency and reliability of diesel engines.
The Future of Diesel Engines
With the increasing focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to more sustainable transportation options, the future of diesel engines may involve advancements aimed at further improving their efficiency and reducing emissions. Technologies such as advanced fuel injection systems, higher-pressure injectors, and improved engine management systems could play a significant role in achieving these goals.
Moreover, there is ongoing research and development in alternative fuels for diesel engines, such as biodiesel and synthetic diesel, which have the potential to reduce the carbon footprint of diesel vehicles even further. These alternative fuels can be used in existing diesel engines without requiring extensive modifications, making them a viable option for reducing emissions in the short to medium term.
While the future of diesel engines may involve advancements and adaptations to meet the evolving environmental standards, their inherent efficiency and reliability make them indispensable in many industries. Whether it’s powering heavy machinery, commercial vehicles, or marine vessels, diesel engines continue to play a significant role in our global economy.
While diesel engines operate differently from gasoline engines and don’t use spark plugs, they utilize the compression ignition principle to efficiently ignite the fuel-air mixture. This unique combustion process, combined with precise injection timing, allows diesel engines to deliver high torque, improved fuel economy, and lower emissions. As technologies and alternative fuels continue to evolve, diesel engines are likely to adapt and remain an essential part of our transportation and industrial sectors.
Do Diesel Engines Use Spark Plugs?
Diesel engines do not use spark plugs like gasoline engines do. Instead, they rely on a different method of ignition to start and run. This is one of the key differences between the two types of engines.
In a diesel engine, the combustion process is initiated by the heat generated from the compression of air in the cylinder. When the air is compressed, its temperature rises significantly, causing the diesel fuel injected into the cylinder to ignite spontaneously.
This process is known as “compression ignition” or “autoignition,” and it does not require a spark plug to ignite the fuel mixture. Instead, diesel engines use glow plugs to preheat the air in the cylinder and facilitate the combustion process, especially when starting a cold engine.
Glow plugs are similar to spark plugs in appearance, but they serve a different purpose. They are designed to heat up the air in the combustion chamber, ensuring that the diesel fuel ignites properly. Once the engine is running, the heat generated by the compression and combustion process is sufficient to keep it running without the need for external ignition.
Key Takeaways
- Diesel engines do not use spark plugs.
- Diesel engines rely on compression and heat to ignite the fuel.
- Spark plugs are used in gasoline engines to ignite the fuel-air mixture.
- In diesel engines, fuel is injected into the combustion chamber at high pressure.
- The compression of the air heats the fuel, causing it to ignite without the need for spark plugs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about diesel engines and spark plugs:
1. What is the purpose of spark plugs in an engine?
Spark plugs are an essential component in gasoline engines. They ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s combustion chamber, creating a spark that leads to combustion and power generation. However, in diesel engines, the ignition process is different and does not require spark plugs.
In diesel engines, fuel combustion is achieved through high compression and temperature, where the fuel self-ignites due to the heat and pressure in the cylinder. As a result, diesel engines do not use spark plugs to ignite the fuel.
2. Why don’t diesel engines use spark plugs?
Diesel engines operate on a different combustion principle compared to gasoline engines. In a gasoline engine, the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug. However, diesel engines have a higher compression ratio, which creates higher temperatures and pressures in the combustion chamber.
Due to the high compression ratio, diesel fuel ignites spontaneously when it is injected into the cylinder, eliminating the need for spark plugs. This spontaneous ignition is known as compression ignition, and it is a fundamental characteristic of diesel engines.
3. What happens if you use spark plugs in a diesel engine?
Using spark plugs in a diesel engine can lead to severe damage and potentially catastrophic failures. Diesel engines are designed to operate without spark plugs, and their combustion process relies on the high compression and temperature to ignite the fuel.
Introducing spark plugs into a diesel engine can disrupt the combustion process and cause misfires, excessive heat buildup, and engine damage. Therefore, it is essential to use the correct components and avoid using spark plugs in a diesel engine.
4. What components are used for ignition in a diesel engine?
In a diesel engine, the ignition of the fuel is achieved through compression ignition, also known as auto-ignition. This process relies on the high compression ratio and temperature generated by the engine’s design.
In addition to compression ignition, diesel engines use glow plugs to aid in cold starting. Glow plugs preheat the air in the combustion chamber, ensuring reliable ignition when the engine is cold. However, once the engine reaches its operating temperature, the glow plugs are no longer needed for ignition.
5. Are there any similarities between diesel and gasoline engines in terms of ignition?
While diesel and gasoline engines differ in their ignition processes, there are some similarities. Both engines require an air-fuel mixture for combustion, and both rely on ignition to initiate the combustion process.
However, the methods of ignition vary. Gasoline engines use spark plugs to create sparks that ignite the air-fuel mixture, while diesel engines rely on compression ignition, where the high temperatures and pressures within the combustion chamber cause the fuel to ignite spontaneously.
How Do Diesel engines run without spark plugs ( #dieselenginecars )
In conclusion, diesel engines do not use spark plugs like gasoline engines do. Instead of relying on spark plugs to ignite the fuel-air mixture, diesel engines use a process called compression ignition. This means that the fuel is injected into the combustion chamber at a high pressure, and the heat generated by compressing the air in the chamber causes the fuel to ignite.
This unique method of ignition is one of the key differences between diesel and gasoline engines. While the absence of spark plugs in diesel engines may simplify the ignition system, it also requires the use of a more robust engine design to handle the higher compression ratios involved. Overall, understanding how diesel engines differ from gasoline engines can help us appreciate the diversity of engine technology and its applications in various industries.
Home - Do Diesel Engines Use Spark Plugs?